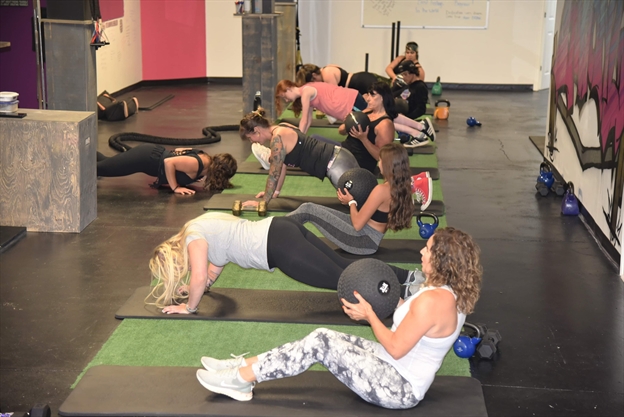
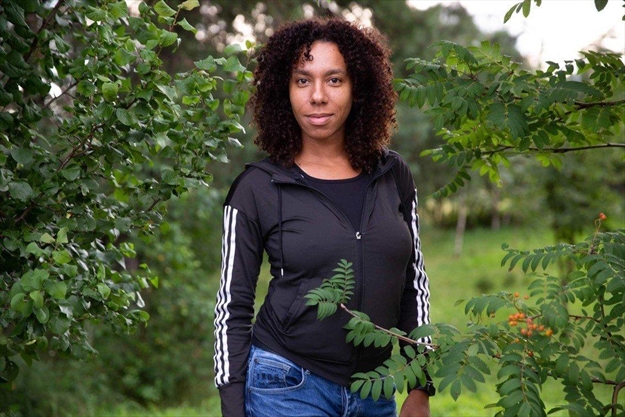
Olympian Hayley Wickenheiser urges Ontario’s gyms to switch to cohorts
Researchers behind a for containing workplace COVID-19 outbreaks say fitness facilities can use the same methods to avoid the fate of , a superspreader event that saw 54 primary cases of the virus last month.
“We have been watching the situation unfold in Toronto around gyms and believe that the use of bubbles … would help the situation,” said Tyler Williamson, one of the nine authors of the Sept. 30 report,
Williams and his co-researchers argue in the report that the use of cohorts or “bubbles” in a workplace can limit potential outbreaks to a small number of employees as long as employees only interact with the people in their given cohort.

If one member of a cohort becomes sick, everyone exposed within that cohort self-isolates while the rest of the workforce continues to work.
Hayley Wickenheiser, who earned four Olympic gold medals as a member of the Canadian women’s hockey team, is currently attending medical school in Toronto and co-authored the Sept. 30 study. She believes that fitness facilities in regions of Ontario not under red zone restrictions can apply the same cohorting principles in two ways: separation in space and separation in time.
While cohorting in space – partitioning one gym into multiple separate facilities and dividing customers and staff between them – might only be feasible for large, open-concept gyms, she said virtually any fitness facility can implement some degree of cohorting in time.
“If you sequester people into time slots, and if you can get people into a more regular schedule without going across times, then you can kind of contain the number of interactions that are taking place between people and reduce the chance that a spreader event will take place over different groups,” she said.
Wickenheiser said gyms where people complete self-guided workouts could accomplish this by dividing operating hours into time slots and having clients sign up for a dedicated, unchangeable time slot each week, so that the same clients are reliably at the gym at the same time.
Facilities that offer pre-scheduled group classes could create more airtight cohorts by having clients commit to a specific class at the same time each week with the same instructor, without the ability to attend a different class. Instructors could be limited to teaching the same one or two classes each week. So if a client in one class tests positive for COVID-19, only that instructor’s one or two classes are potentially impacted, rather than the entire studio.
While this strategy would limit flexibility for staff and clients, Wickenheiser believes it’s worth it to provide the ability to prevent a facility-wide closure.
“We all have to be able to give up a little and sacrifice and if that’s what it takes to keep gyms going,” she said.
Chelsi Rodrigues owns and operates Whole Health Strength and Fitness, a small fitness centre in Cambridge. She believes the system Wickenheiser and her co-authors recommend should be workable for most gyms the size of hers.
“It’s not unrealistic, what they’re proposing,” she said. “At the end of the day, I don’t think anyone wants to get the virus.”
Rodrigues already offers scheduled fitness classes for up to 10 participants and uses a software application to keep track of everyone who enters the facility. None of her staff or clients have tested positive for COVID-19.
Her biggest challenge would be in staffing. Most of her trainers teach two classes per week, while her own class schedule is full. In order to further limit her contact with clients, she would need to hire additional staff.
“It would be more of a challenge for me because I’d have to step back and have them come in more,” she said.
Brian Fehst sits on the board of directors of the Ontario Society for Health and Fitness. He also believes sole-proprietor fitness centres might find it financially challenging to separate staff into cohorts, but said most would be willing to adopt the new strategy if it were ever mandated by public health.
“I think we’re already seeing a lot of acceptance of what the guidelines are and the facilities are really buying into it,” he said. “They’re saying, ‘This is important to protect our community health, so we’re going to be compliant.’”
For more information about the province’s COVID-19 guidelines for fitness facilities, visit .